Welding procedure qualification is a key requirement to ensure the structural integrity of welded components, confirming that joints meet both regulatory and operational standards. In this context, mechanical, chemical, and metallographic testing plays a critical role in validating welding parameters and ensuring compliance with technical specifications.
Applying these tests rigorously helps detect potential discontinuities, evaluate material strength, and verify weld fusion quality and microstructure. This ensures that the welding process is reliable and repeatable, preventing premature failures and extending equipment lifespan.
Applied Methodology
The tests typically used for welding procedure qualification include:
Mechanical Testing:
- Tensile testing to determine strength and ductility;
- Charpy impact testing to evaluate material toughness;
- Hardness testing to assess hardness distribution across the weld zone;
- Bend testing to verify weld ductility and identify surface or internal discontinuities.


Chemical Testing:
- Optical emission spectrometry (OES) to determine the chemical composition of base and weld metals.
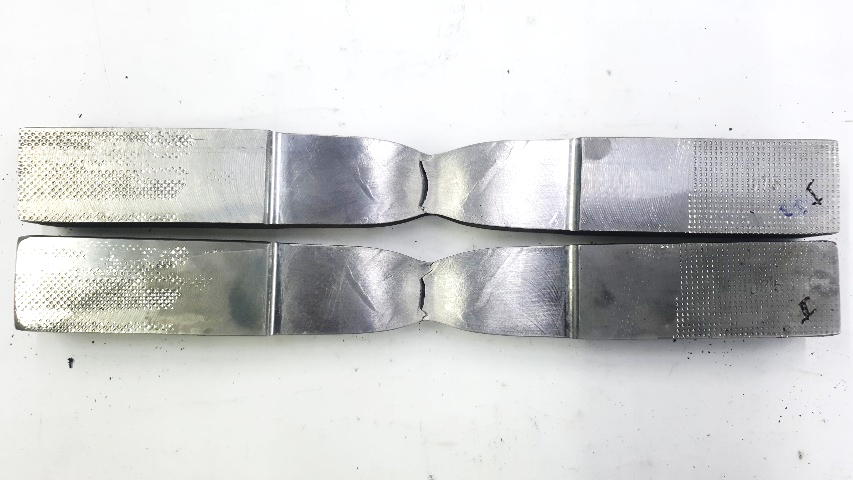
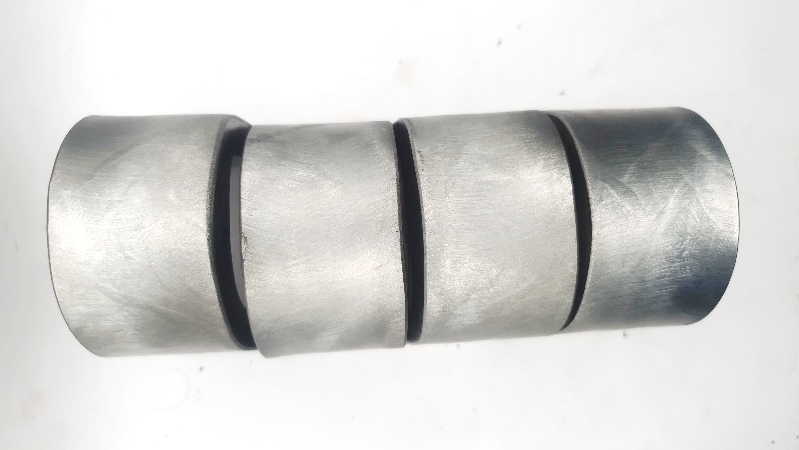


Metallographic Testing:
- Macroscopic examination to assess weld penetration and identify visible discontinuities;
- Microscopic analysis to evaluate the microstructure of the weld metal and heat-affected zone (HAZ);
- Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) to identify failure mechanisms and localized chemical variations.
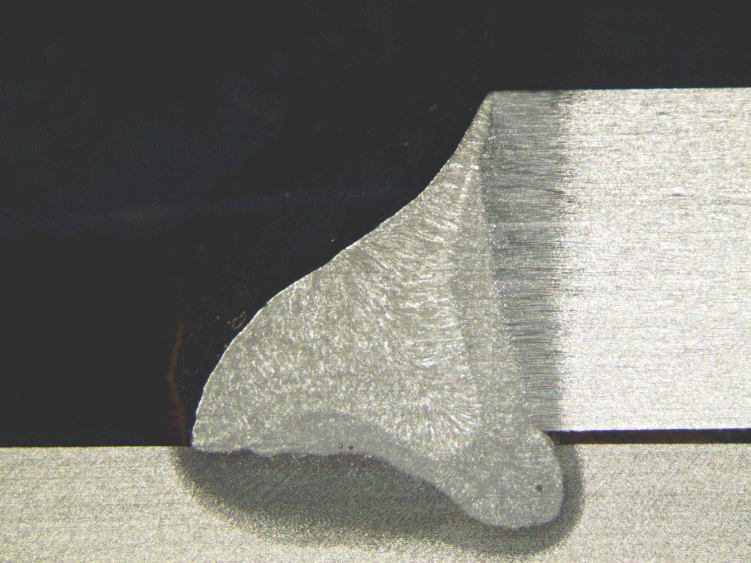
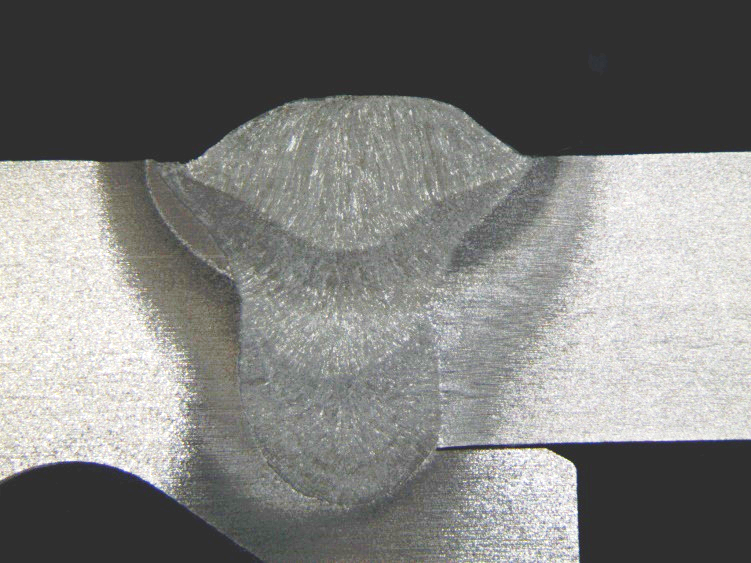
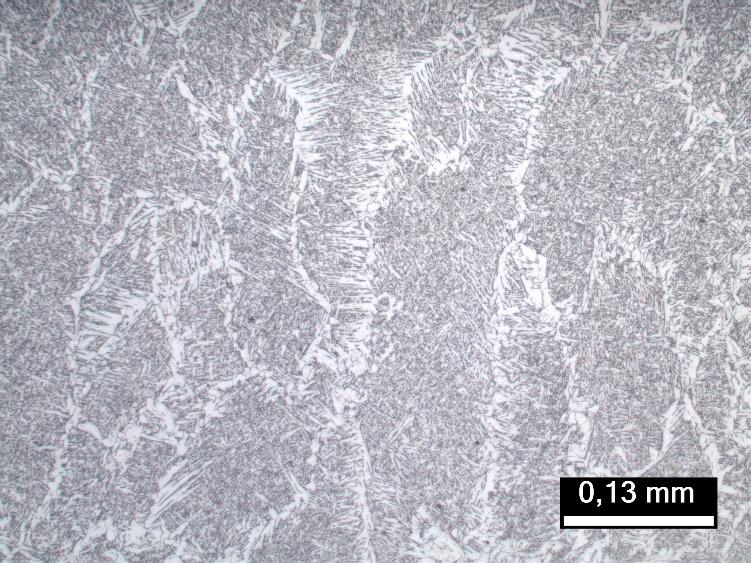
Results
Welding procedure qualification using these methods ensures that the welded joint meets the required mechanical properties, has a compliant chemical composition, and presents a microstructure that supports structural integrity. Early detection of potential failures enables adjustments to the welding process before large-scale application, reducing rework and operational risks.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Mechanical, chemical, and metallographic testing is essential for qualifying welding procedures and ensuring weld quality and reliability. To ensure safety and compliance, we recommend:
- Performing tests according to application-specific standards;
- Continuously monitoring welding quality through periodic inspections;
- Training professionals involved in welding and inspection processes;
- Using advanced analysis methods to improve welding practices.

